Being a client-side scripting language, JavaScript needs some clients to interpret and execute it. In the case of web applications, we can use any of the supported web browsers as a platform for executing JavaScript. In the below sections, let's understand how does JavaScript run in a web browser and how the JavaScript engine interprets the JavaScript code. Moreover, we will also understand how JavaScript can integrate under various sections of an HTML page.
-
How does JavaScript run in a web-browser?
-
How to embed and execute JavaScript in a web-browser?
-
Procedure to embed and execute JavaScript in the HTML
<body>tag? -
How to embed and execute JavaScript in HTML
<head>? -
How to embed an external JavaScript file in HTML?
-
-
Procedure to diagnose an error in JavaScript?
How does JavaScript run in a web-browser?
JavaScript is an interpreted language where code is explained and executed at the runtime. Additionally, we know that web browsers understand HTML and CSS and converting those languages into a visual display on the screen. The part of the web browser that understands HTML and CSS is called the rendering engine. However, most browsers also have a JavaScript interpreter. That’s the part of the browser that understands JavaScript and run JavaScript programs. A typical architecture of a browser looks like below:
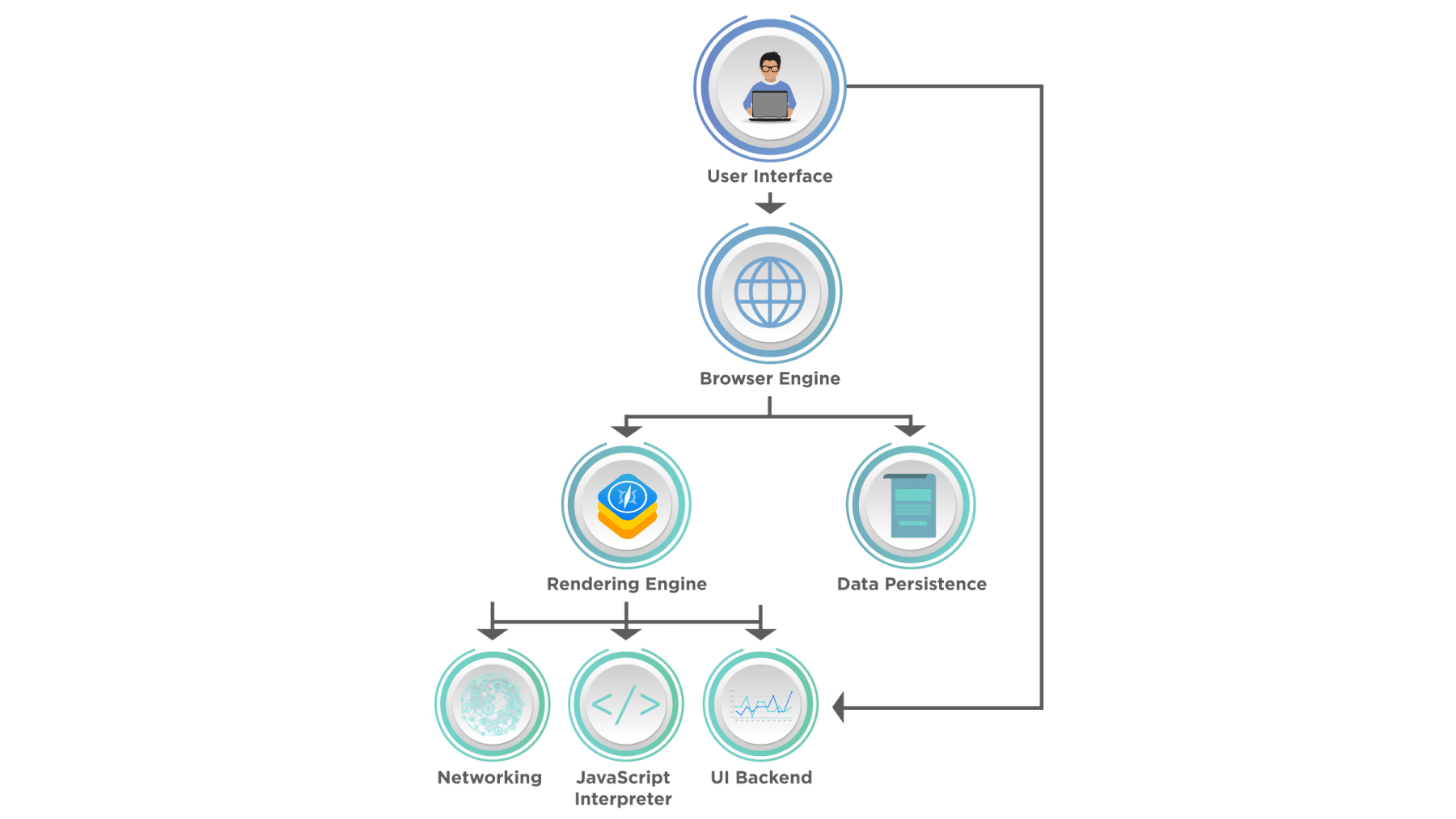
As we can see, the browser's Rendering engine interacts with the "JavaScript's Interpreter" and sends the JavaScript code to the JavaScript engine for processing.
The JavaScript engine/JavaScript Interpreter comprises both an Interpreter and a Just in Time compiler. Additionally, the overall execution of the JavaScript is a 5 step process, as shown in the below image:
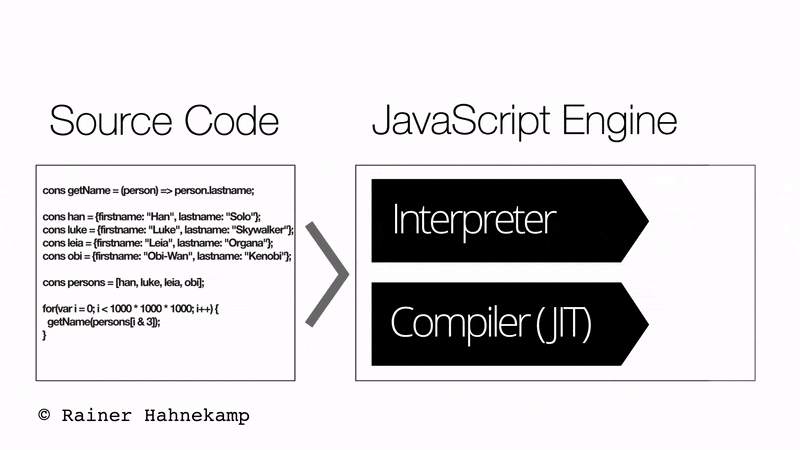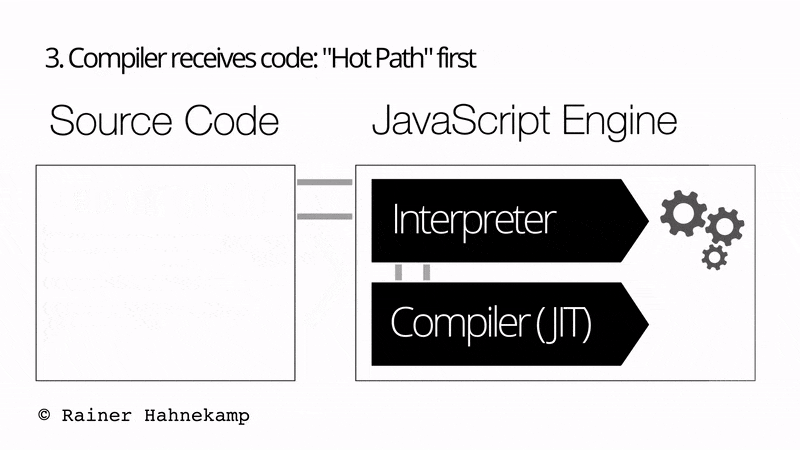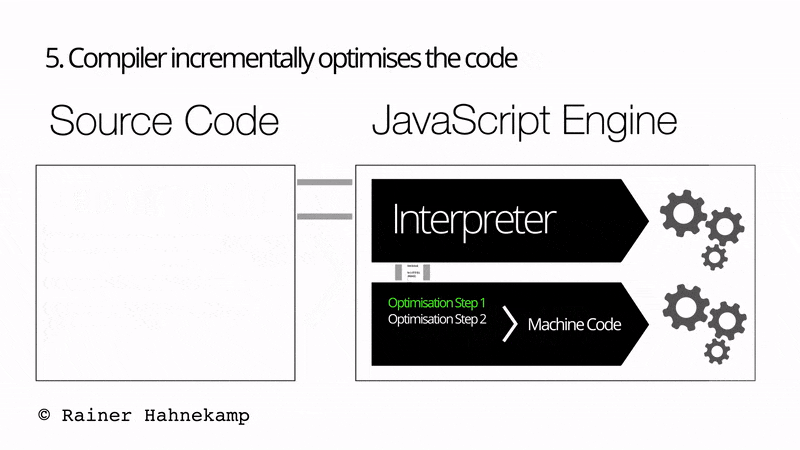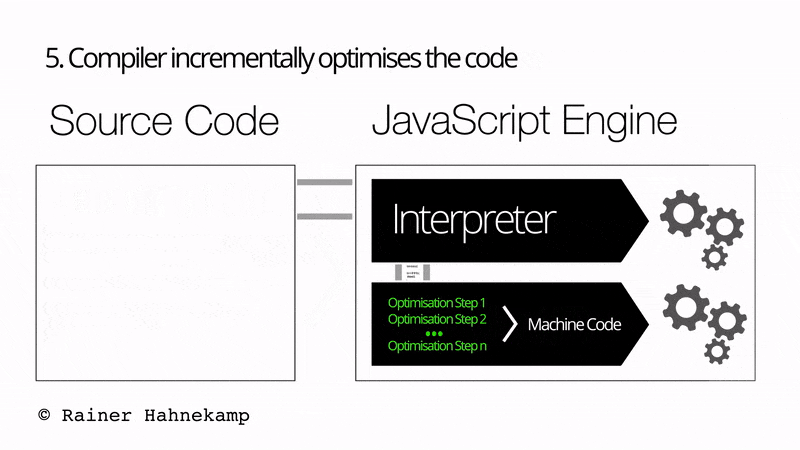
- JavaScript Engine Loads Source Code.
- The interpreter starts the application.
- The Compiler receives code.
- The compiler starts optimization and compilation.
- The compiler incrementally optimizes the code.
Now when we talk about JavaScript engines, each of the browsers have their pre-installed engines. Below are few of the JavaScript engines developed and used by some major browsers:
- V8 Engine: This engine is developed by Google, which is one of the most used Engines in chrome, chromium, and even in NodeJS.
- Spider Monkey: Mozilla developed this engine used in the Firefox browser.
- JavaScriptCore: This engine s developed by Apple used in the Safari browser.
- Chakra: Microsoft developed this engine used in the Edge browser and internet explorer.
- Hermes Engine: Facebook developed this engine used in android apps.
How to embed and run JavaScript in a web-browser?
The web browser is usually expecting HTML, so you must specifically tell the browser when JavaScript is coming by using the <script> tag. The
<script> tag is regular HTML tag. In addition to this, it acts like a switch that, in effect, says, “Hey, web browser, here comes some JavaScript code; you don’t know what to do with it, so hand it off to the JavaScript interpreter”. When the web browser encounters the closing </script> tag, it knows it’s reached the end of the JavaScript program and can get back to its normal duties. Let's understand in following sections, how the JavaScript code embeds inside an HTML file:
How to embed and execute JavaScript in the HTML <body> tag?
The <script> Html tag enables the integration of JavaScript code directly within the <body> tag.The JavaScript code will lie under <script> tag, and the browser automatically executes the script once a page is loaded.
The below code demonstrate the “Hello world!” program using JavaScript written directly inside <body> tag.
<html>
<head>
<title>My First Program</title>
</head>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
document.write("Hello World!")
</script>
</body>
</html>
Open any text editor like notepad++ and type the above code. Save the file with name helloworld.html and open it in any browser (Chrome, Firefox, or IE). It should show the output as:
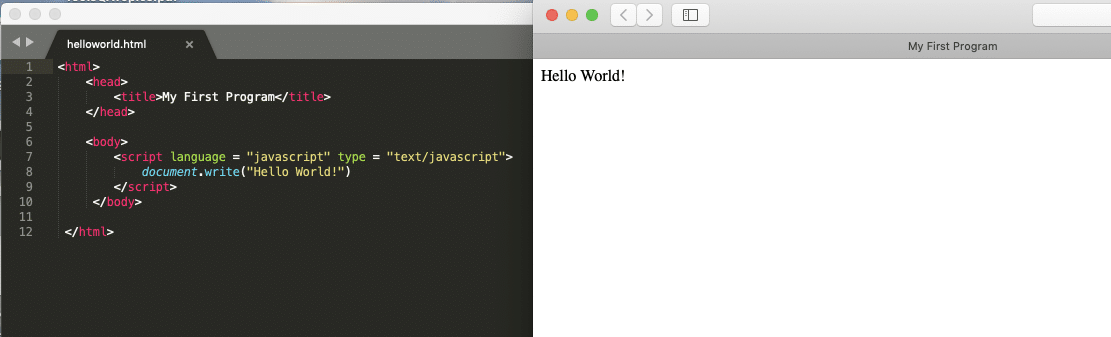
As seen in the above example, "document.write" is a function used to write data into the Html page. When we open an Html file in the browser, the JavaScript present under script tag executes. We will discuss more details above other functionalities, like write in the DOM Manipulation article.
How to embed and run JavaScript in HTML <head> tag?
The <script> html tag can be used to define a function under the
<head> tag of HTML. The JavaScript code will lie under <script> tag in a function which can be invoked inside the <body> tag of HTML.
The below code demonstrate the “Hello world!” program using JavaScript written under the <head> tag.
<html>
<head>
<title>My First Program</title>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
function myFunction() {
document.write("Hello World!");
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>myFunction()</script>
</body>
</html>
Write the above code in a text editor and save the file with the name helloworld2.html. Later open it in any browser.
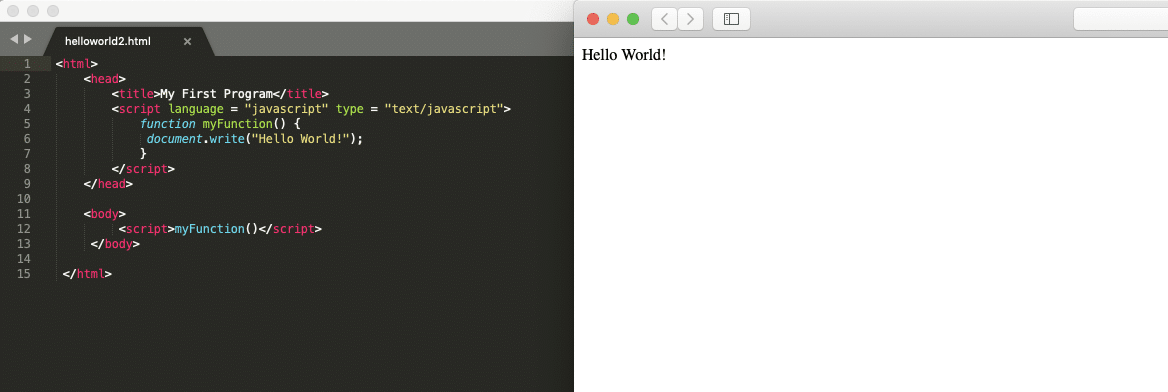
In the above example, we created a function in the header and called that function in the body tag. At this moment, don't worry about what is a function and it's usage because we will cover it in functions article.
How to embed an external JavaScript file in HTML?
Apart from the above ways of integrating JavaScript in the HTML, we can save the JavaScript as a separate script file with .js extension and include the same inside the HTML code using the src attribute of the <script> tag. By doing this, we can reuse the same JavaScript code in multiple HTML files.
The below code demonstrates the “Hello world!” program using JavaScript written as an external file.
function myFunction() {
document.write("Hello World!");
}
Save the above JavaScript code as ext.js file. Invoke the above JavaScript in the below HTML using the src attribute of <script> tag.
<html>
<head>
<title>test</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="ext.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">myFunction()</script>
</body>
</html>
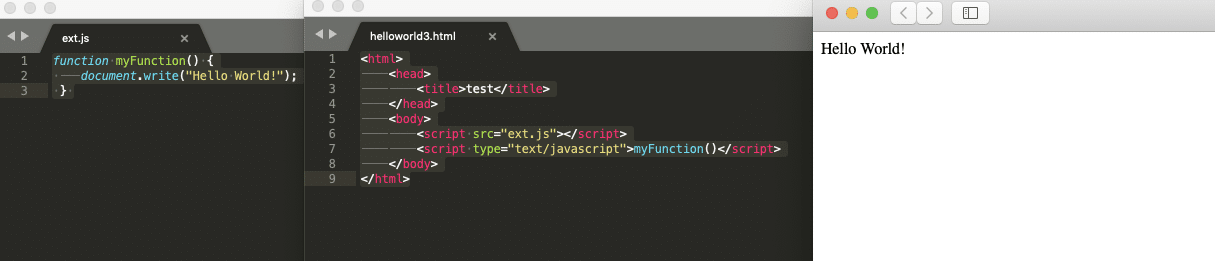
Note: The src attribute will specify the absolute path of the JavaScript file.
In the above example, we have created javascript in a separate file and used that file in Html with the help of an src tag, which imports JavaScript code in the provided file at runtime.
How to diagnose an error in JavaScript?
When the website loads but does not display correctly, this is due to a coding error on the site. Usually, JavaScript causes it or CSS errors. If you have JavaScript on your website that is not working, you can diagnose them by using your browsers "Error Console". Each browser has a built-in “Error Console” for diagnosing scripting errors on your site.
To understand the "Error Console" in detail, let's consider the code snippet below. Whereby we have explicitly introduced an error by removing the double quotes from the string "Hello World!" while passing the same to the document.write() method:
<html>
<head>
<title>My First Program with Error</title>
</head>
<body>
<script language = "javascript" type = "text/javascript">
document.write(Hello World!)
</script>
</body>
</html>
Save the file with name firstProgramWithError.html and open it in a browser. It should show the output as:
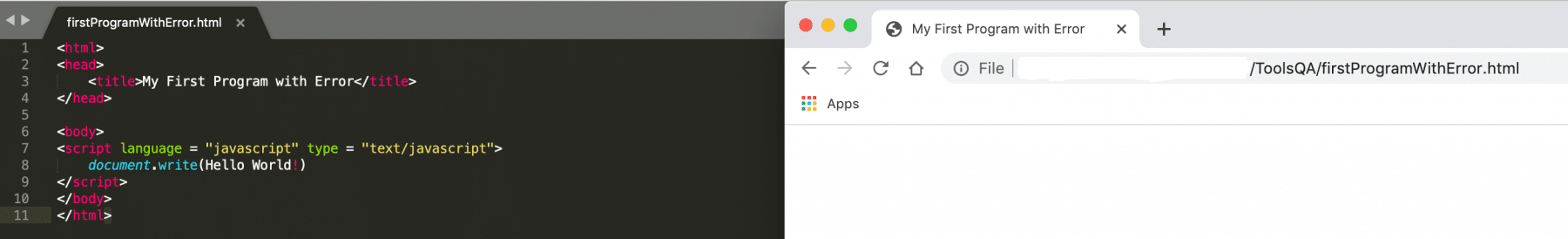
As we can see from the above screenshot that nothing is there on the HTML page. As a result, this makes it skeptical that there's something wrong, as the output is not as expected. So, how to check what the error is? One can check this error with the help of the browser's "Error Console". Let's consider we are using "Chrome" viewing our program. So, we can open the "Error Console" in chrome using the following steps to view the error raised by our program:
1. Firstly, Right-click anywhere in the browser's viewport to open the context-menu as below:
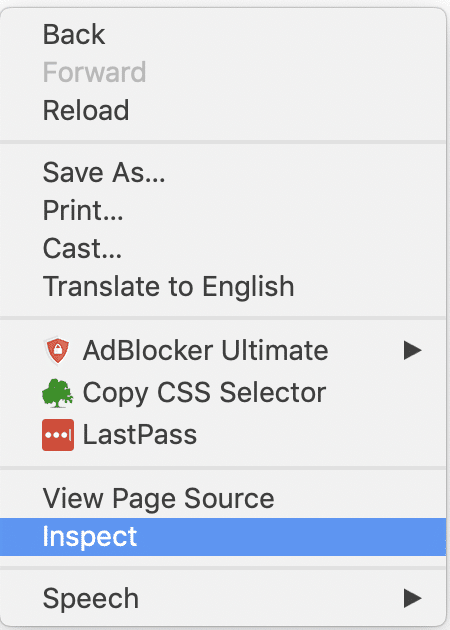
2. Secondly, click on the "Inspect" item in the Context Menu." It will open chrome-dev tools. Select the "console" tab as highlighted in below screenshot:
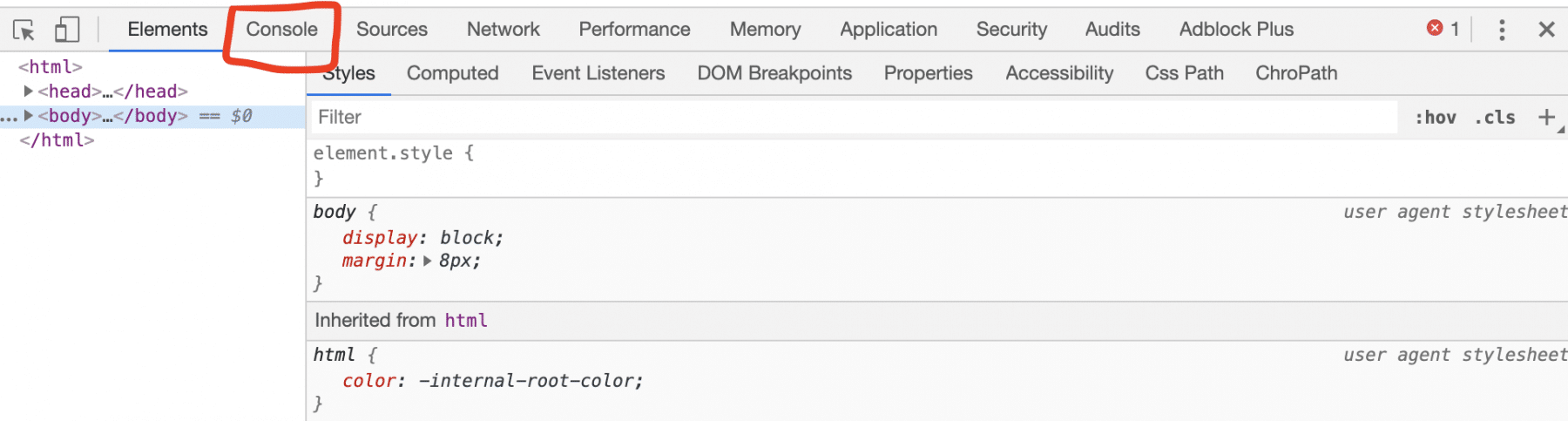
3. Finally, if we again open the above firstProgramWithError.html file in chrome, it shows the output as below:
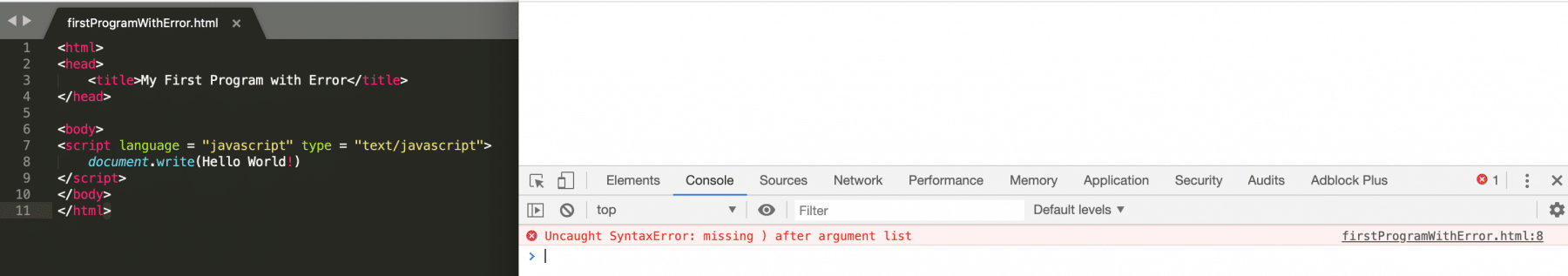
4. So, it shows the error in the "Console" tab and mentions the error is in "line 8" of the file.
Therefore, a user can quickly diagnose any error, if there, in the JavaScript code. Similarly, other browsers also provide the "Error Console" windows. Which, in turn, diagnose the JavaScript errors whenever an error arises in a specific code of JavaScript.
Key Takeaways
- A developer can use
<script>tag of HTML to write JavaScript code inside an HTML file. - In addition to this, the
<script>tag can be integrated inside various sections like<body>,<head>of the HTML file. - *Finally, the "Error Console" windows of browsers can diagnose any JavaScript errors
Let's now move to the next article where we will learn about concepts of data types and variables in JavaScript.