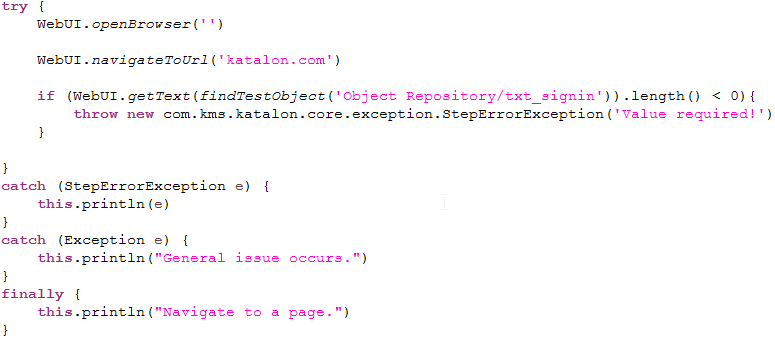
Katalon Studio provides the ability to dictate the logical flow of execution by supporting control statements such as If/Else, for/while or Try/Catch… which are very common concepts in programming language. This tutorial will explain in details how to use control statements in Katalon Studio along with examples for each case.
The following control statements are supported in Katalon Studio:
- Decision-making statements (https://goo.gl/BDn5JY)
- Looping statements (https://goo.gl/a5YHHS)
- Branching statements (https://goo.gl/cMX373)
- Exception handling block (https://goo.gl/XFYhGt)
Note: once a test step is added as any of the control statements, it will not be allowed to change it into another keyword.
Decision-making statements
In Manual View
Open a test case in Manual view, then navigate to Decision-making Statements from the command toolbar.
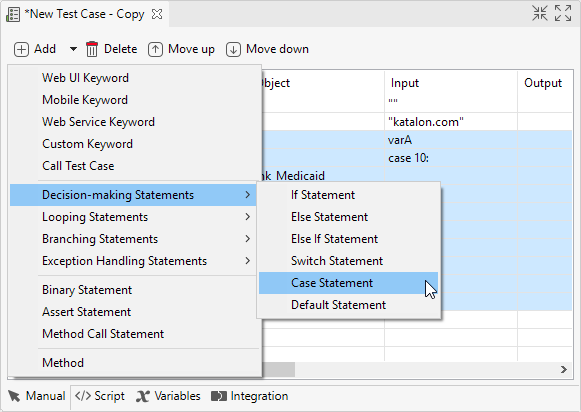
Refer to the following table for the usage of each statement:
| Statement | Description |
|---|---|
| If | This statement requires a boolean condition as input value. Katalon Studio will execute all the steps within once the condition is triggered. |
| Else If | Using Else If after If, you can create a combination of conditions where the steps within the first satisfied condition will be executed. |
| Else | This statement serves as the conclusion of the If – Else If – Else structure. The steps within this statement will be executed if all the conditions above it are not triggered. |
| Statement | Description |
|---|---|
| Switch | This statement requires an expression, which is often referred to as the control expression (or control variable), as input value. |
| Case | The Cases indicate the assumed value for the control expression, with corresponding steps to be executed when a match occurs. Each Case will have a Break by default which should be positioned at the end of the Case block to mark the end of it. |
| Default | This statement is included automatically within every Switch statement. In the situation in which noCase value can be matched, the steps within Default will be taken. |
In Script View
The Script view of test cases allows you to programmatically define and handle If-ElseIf-Else or Switch-Case structure easily using either Groovy or Java language. Refer to conditional structure (http://groovy-lang.org/semantics.html#_conditional_structures) in Groovy for more details.
For example:
| Decision-making statement | Screenshot |
|---|---|
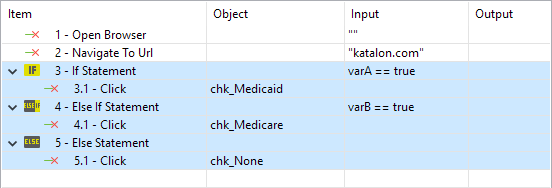
| If - Else If - Else | Here is an example on how to use if-else if-else in Scripting View where the Click action will be carried out based on the condition ! 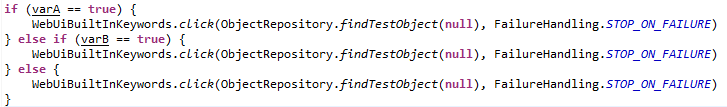 |
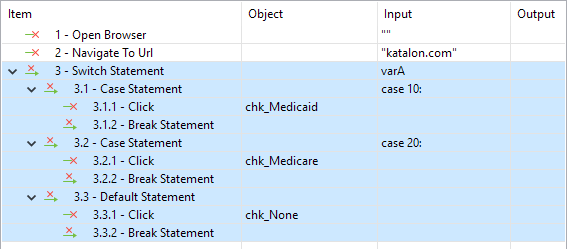
| Switch - Case | Here is an example on how to use switch-case in Scripting View where the value B will be calculated based on the passing value of variable A !  |
Looping statements
In Manual View
Open a test case in Manual view, then navigate to Looping Statements from command toolbar.
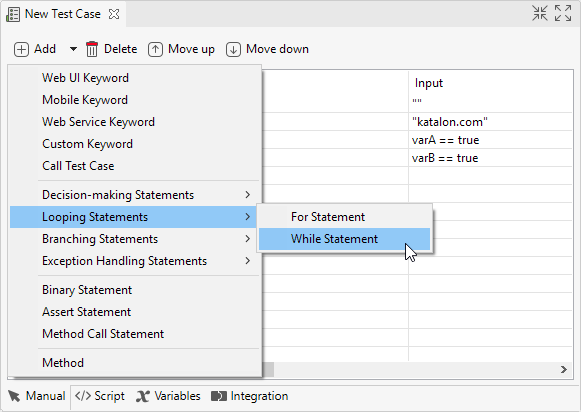
Refer to the following table for the usage of each statement:
| Statement | Description |
|---|---|
| For | This statement accepts a range, list or array as input value so that Katalon Studio knows how many times to execute all steps within the For structure. |
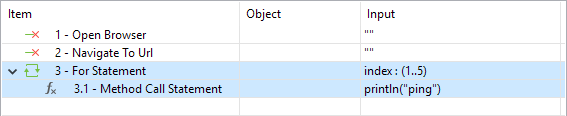
| Statement | Description |
|---|---|
| While | This statement requires a boolean condition as input value so that Katalon Studio will keep executing all steps within until the condition fails. |
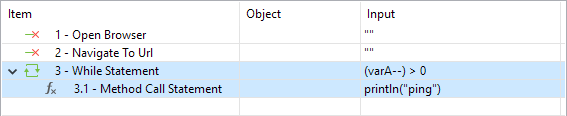
In Script View
The Script View of test cases allows you to programmatically define and handle For or While structure easily using either Groovy or Java language. Refer to looping structures (http://groovy-lang.org/semantics.html#_looping_structures) in Groovy for more details.
For example:
| Looping statement | Screenshot |
|---|---|
| For | Here is an example on how to use For in Scripting View where the acceptAlert keyword will be executed 10 times |
| While | Here is an example on how to use For in Scripting View where the value of varA is true 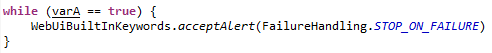 |
Branching statements
In Manual View
Open a test case in Manual view, then navigate to Branching Statements from command toolbar.
Refer to the following table for the usage of each statement:
| Statement | Description |
|---|---|
| Break | Katalon Studio will exit current code block and continue to next code block/test step. |
| Statement | Description |
|---|---|
| Continue | Katalon Studio will skip the remainder of the current loop and continue with the next iteration of the loop. |
| Statement | Description |
|---|---|
| Return | Katalon will exit from the current method/step, and the flow control is returned to where the method/step was invoked. |
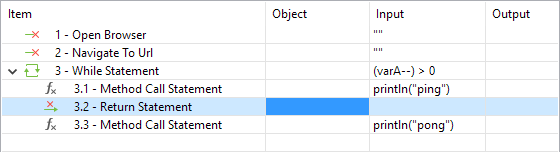
In Script View
The Script view of test cases allows you to programmatically define and handle Break, Continue & Return easily using either Groovy or Java language.
For example:
| Decision-making statement | Screenshot |
|---|---|
| Break | Here is an example on how to use Break in Scripting View in order to exit current code block and move to next code block. 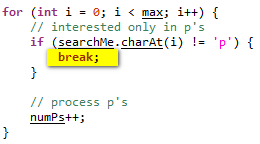 |
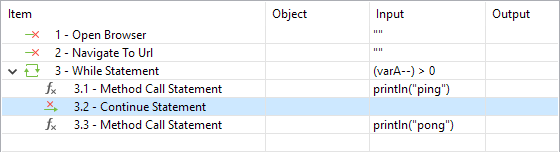
| Continue | Here is an example on how to use Continue in Scripting View in order to skip the remainder of the current loop and continue with the next iteration of the loop.Common Condition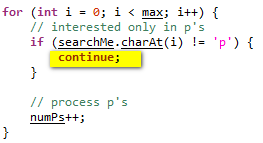 |
| Return | Here is an example on how to use Return in Scripting View in order to exit from the current method, and the flow control is returned to where the method was invoked.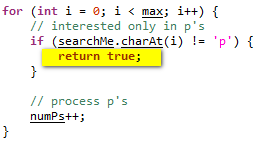 |
Exception handling block
In Manual View
Open a test case in Manual view, then navigate to Exception Handling Statements from command toolbar.
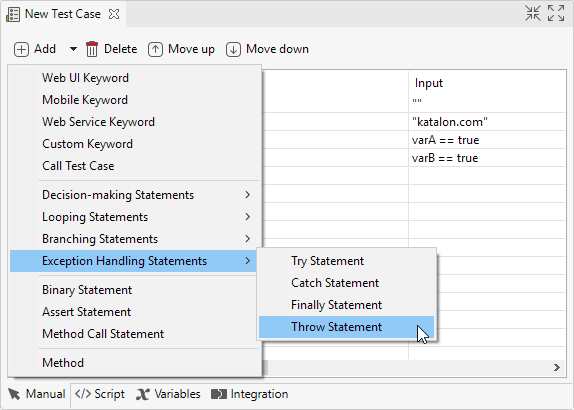
Refer to the following table for the usage of each statement:
| Statement | Description |
|---|---|
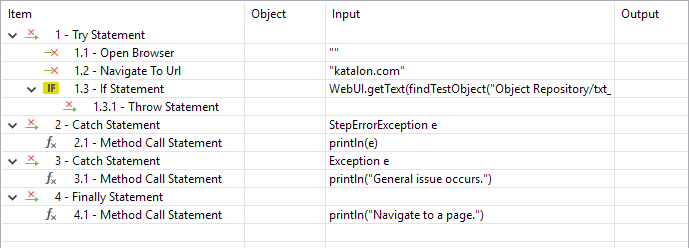
| Try | This statement indicates that all steps within will be monitored by exception handlers. |
| Throw | Before you can Catch an exception, some code must throw one. Regardless of what throws the exception, it's always involved with the Throw statement |
| Catch | Katalon Studio will execute all steps within when there is any issue occurred during execution of the Try block. |
| Finally | This is the last part of the Try-Catch-Finally structure and all steps within this will be executed regardless of any exception. |
In Script View
The Script view of test cases allows you to programmatically define and handle exception easily using either Groovy or Java language. Refer to this guide for more details about exception handling in Groovy.
For example: