We have seen the structure of the Python course in the previous article. As I mentioned before, reading this article will help you to understand Programming and Python in a better way.
We are going to see the following topics one by one.
- What is Programming?
- Basic terminology in Programming Language
- How to execute Programs?
- Interpreter Vs. Compiler
- What Next?
What is Programming?
Writing a set of instructions for a specific task to be done by the computer is known as Programming. Computers are fast, cheap, and handy to do the repeated tasks any number of times. We can get bored by doing the same job repeatedly. But, the computer will do the same task any number of times with high accuracy and lightning speed.
Do computers complete a task by themselves?
No, they can't perform without the help of humans [Maybe yes shortly]. We have to give instructions to the computer to perform specific tasks.
For example, if we have to find the area of a square. We will have a side length a and the formula for the area of the square is a2. But, the computer doesn't know about the dimension of the side and the formula to calculate the area. Therefore, we have to give specific instructions to the computer so that it knows the size of the side (value a) and the method to calculate area ( a2).
Basic terminology in Programming Language
Before we go through Python coding, and all the good stuff that comes with it, it's essential to understand how the computers understand the program that humans write. Hence, we will go through some basic terminology and concepts that will make your foundation concepts robust. Additionally, you can apply these concepts to any programming language and not just python. So without further ado, let's get started!
What is a Programming Language?
Computers don't understand our languages like English, Hindi, French, Spanish, Chinese, Japanese, etc. Computers only understand 0's and 1's. The vocabulary, which consists of 0's and 1's, is called Machine Language. It's challenging for us to write instructions in 0's and 1's. Therefore, we humans created a style to give instructions to the computers for the completion of specific tasks, i.e., Programming Language. Programming languages are also known as High-Level Languages, which can be understood by human beings. Additionally, machine language is also known as Low-Level Language.
Some of the programming languages are C, Java, C++, etc.
There is another language called Assembly Language, which converts our human-readable code, i.e., programming language to an assembly level language. Assembly language is also known as the low-level language. It is mostly used for microprocessors and programmable devices, which directly deals with the hardware. In addition to this, we don't have to know much about assembly level language now. You can take the help of the internet in case you need to learn more about it.
Examine the pic for more clarity.

What is a Program?
A set of instructions that a computer executes is known as a Program. The collection of instructions is also known as the Instruction list [IL]. It's a file that has separate extensions like .c, .py, .java, etc., for C, Python, Java respectively. Below is an example program to calculate the area of the square.
# square one side length
side = 4
# calculating the area of the square
area = side * side
# displaying the square area
print(area)
Don't worry about the program. We will learn to write programs in subsequent articles.
The program or instructions which we are trying to write in a high-level programming language is also known as source code. There are many names for the code we write. Please make sure you don't get confused with the names.
Terminology
Every language, including Natural Languages, which we are using in our daily conversations, has some rules to follow. Let's see them one by one.
-
Alphabets
- Any language in this world has a particular set of symbols to form words.
- English has Latin alphabets, Japanese has Kanji, so on and so forth.
- Moreover, Alphabets are building blocks of the language.
-
Lexis
- A collection of words that a language has to create sentences.
- Prepositions, Articles, etc. in English.
- In programming, we call them as keywords. Every programming language has a set of predefined words that we need to use to write instructions.
-
Syntax
- A set of rules to examine whether the sentence is valid or not.
- We need to arrange the words of a language in a well-defined format to form correct sentences.
- For example, the sentence, "Are you how?" doesn't have valid syntax. Whereas the sentence, "How are you?" does.
- In the same manner, we need to write instructions for the computer that are valid and should be understood by the computer.
- Moreover, the arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences in a language happens.
- In the context of computers, it refers to the proper ordering of symbols and codes which, in turn, helps the computer to understand what instructions are telling it to do.
- Semantics
- A set of rules to examine whether a phrase is making any sense or not.
- We need to create sentences that make sense to use. For example, the sentence Statue of liberty is moving doesn't make any sense. However, the syntax of the sentence is correct.
- Therefore, in programming, we need to make sure our instructions are well semantic.
We will know more about the above terminology in terms of programming in detail when we start writing the code. Don't bother about the vocabulary, even if you don't understand it now.
How to execute Programs?
Now that we have written a program, what to do with it. We have to run it to get the output. Previously we have written a program to calculate the area of a square but didn't execute it. Therefore, when you run it now, you will have a result according to your code. In the above program, you will get 16 as output. To execute our programs, we need a tool i.e., Compiler, or Interpreter. Let's explore them.
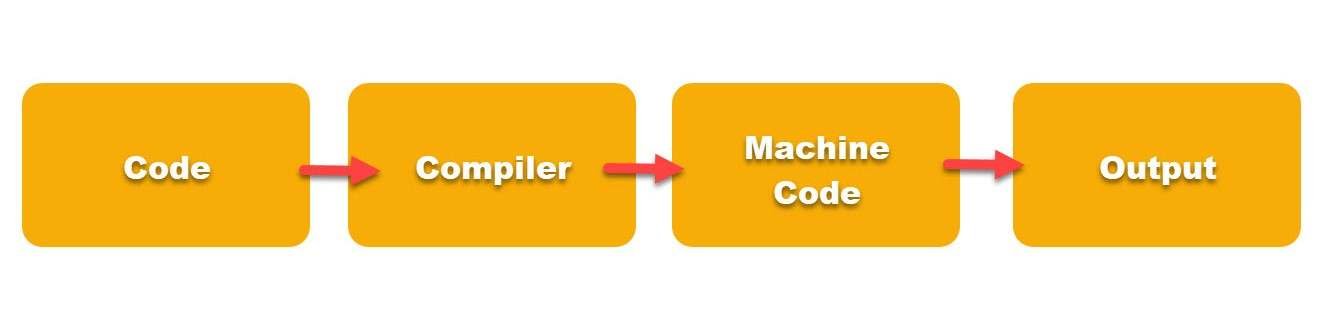
What is a Compiler in Programming?
- A compiler takes the set of instructions you have written and validates them according to the language syntax. If everything is good, it will give you the output.
- The compiler will throw errors if the code is not valid.
- Moreover, different programming languages have different compilers.
- Languages like C, C++, etc. use the GCC compilers respectively to execute the programs.
- We will have multiple compilers for one programming language. Users will choose according to their needs.
- Additionally, the compiler will go through different stages in the execution process.
- In the end, it converts the instructions into Machine Language that can be understood by the computer.
- It generates an executable file. Therefore, we don't have to execute the program every time to see the result.
- See the below illustration.
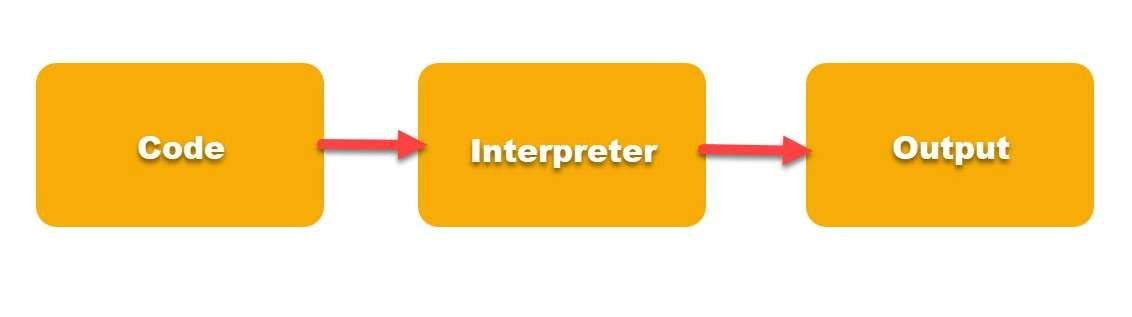
What is Interpreter in Programming?
- An interpreter is also similar to the compiler. It validates the syntax and gives you the result if everything is correct.
- Languages like Python, Perl, etc. use the interpreter.
- It converts the source code into an intermediate form and then executes it.
- Additionally, we have to run the program every time to see the result.
- See the illustration.
When both compiler and interpreter execute the programs, then what's the difference between them? Let's examine the differences between them.
Difference between Interpreter and Compiler
| Attributes | Interpreter | Compiler |
|---|---|---|
| Execution | 1. One Statement at a time.2. Compilation and Execution will occur at the same time. | 1. All statements at once. 2. Execution starts after the compilation of the code. |
| Execution Speed | Slower compared to Compiler | Faster than Interpreter |
| Error Handling | Halt the program whenit finds an error. | Displays all errors at the end of the program. |
| Memory | It requires less memory as it compiles and executes at the same time. | The compiler takes more memory compares to the Interpreter for the compilation and execution. |
| Error Correction | Easy | Hard compared to Interpreter. |
| Programming Languages | Python, Perl, Ruby, Matlab, etc. | C, C++ , C# |
What Next?
To conclude, we have learned a lot from this article. Knowing this basic stuff is essential before moving into the actual programming for beginners. In the following tutorial, we are going to know some more exciting things about Python Basics.
I hope you enjoyed the tutorial. If you have any doubts regarding the tutorial, please mention them in the comment section.
Happy Coding :)