What is Software Development Life Cycle - SDLC?
Software Development Life Cycle is a systematic approach to develop software. It creates a structure for the developer to design, create and deliver high-quality software according to the requirements of customer or end-user. It also provides a methodology for improving the quality of the desired product. The purpose of SDLC process is to provide help in producing a product that is cost-efficient and of high quality.
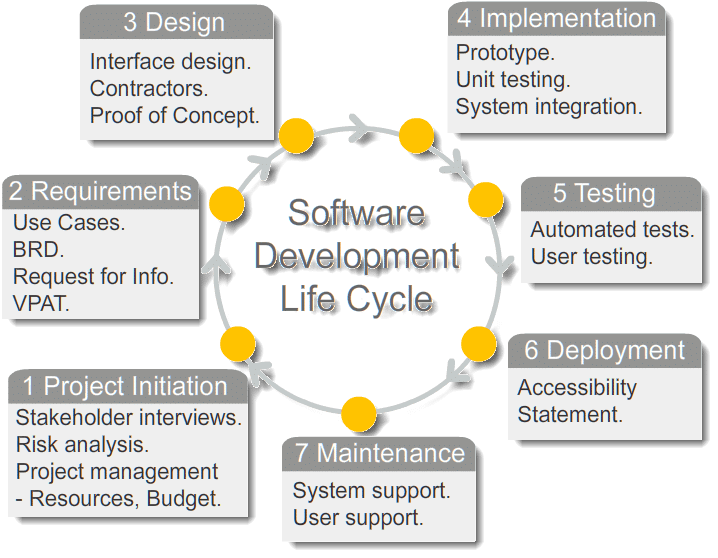
Different Stages of Software Development Life Cycle
Stage 1: Planning of Project:
This includes making reasonable estimates of the cost and size of the software product as compared to the resources at hand.
Stage 2: Analysis & Requirement Gathering
This step includes collecting maximum information from the client about the desired product. All details and specifications of the product must be discussed with the customer. The development team analyses the requirements keeping in view the design and coding of the software. The requirements so gathered are then analyzed for their validity and the possibility of incorporating them into the software system. The aim of requirement analysis is to capture the detail of each requirement so that everyone understands how each requirement is to be worked.
Stage 3: Design
In this phase, the program developer analyses whether the software can be prepared to fulfill all the requirements of the end-user. Also, he checks that the project is financially, practically and technologically feasible for the customer. After that best design approach is selected for the product. The developer selects the program language like Java, Oracle, etc. which will be best suited for the software. It is also like the engineering representation of the product to be built.
Stage 4: Development or Implementation
It means translating the design into a computer-readable language. The development team does the actual coding based on designed software and writes unit tests for each component to test the new codes written by them. The developer may show the work done to the business analysts and the modification or enhancements may be required. This is the longest phase of SDLC.
Stage 5: Testing
This is the last phase of SDLC before the software is delivered to the customer. The job of the test team is to test the system against the requirements. The aim of a tester is to find out the gaps or defects within the system and also to verify that the software works as expected according to the requirements. It includes Unit testing, Integration testing, and System testing.
Stage 6: Deployment
Once the product is tested and ready to deploy, it is released to consumers to use. The size of the project will determine the complexity of the deployment if required. The users can be trained on, or aided with the documentation on how to operate the software. A small round of testing is also performed on production to make sure of any environmental issues and any impact of new release.
Stage 7: Maintenance
When the customers start using the developed system, the actual problems come up and need to be solved from time to time. This process where the care is taken for the developed product is known as Maintenance. The software is maintained timely by updating the code according to the changes taking place in the user end environment or technology.
Different types of Software Development Life Cycle
- Waterfall Model: The waterfall model is a sequential design process, used in software development processes, in which progress is seen as flowing steadily downwards (like a waterfall) through the phases of conception, initiation, analysis, design, construction, testing, production/implementation and maintenance. Learn More
- Iterative Model: Iterative development is a way of breaking down the software development of a large application into smaller chunks. In iterative development, feature code is designed, developed and tested in repeated cycles. Learn More
- Spiral Model:Spiral model is a combination of iterative development process model and sequential linear development model i.e. waterfall model with very high emphasis on risk analysis. It allows for incremental releases of the product, or incremental refinement through each iteration around the spiral. Learn More
- V-Model: In software development, the V-model represents a development process that may be considered an extension of the waterfall model, and is an example of the more general V-model. Instead of moving down in a linear way, the process steps are bent upwards after the coding phase, to form the typical V shape. Learn More
- Big Bang Model:The Big Bang model is SDLC model where we do not follow any specific process. The development just starts with the required money and efforts as the input, and the output is the software developed which may or may not be as per customer requirement.
- RAD Model: The functional modules are developed simultaneously as prototypes and are integrated to make the complete product for faster product delivery. The customer gets early visibility in the software and can provide feedback on design, delivery, and other requirements. Learn More
- Prototype Model: The basic idea here is that instead of freezing the requirements before a design or coding can proceed, a throwaway prototype is built to understand the requirements. This prototype is developed based on the currently known requirements. Learn More











